Time:2016-05-13
The recent outbreak of ZIKV infection in the Americas, in particular Brazil, is accompanied by a marked increase in cases of microcephaly of newborns. On the basis of the potential threat of ZIKV infection to central nervous system development of infants, the World Health Organization declared in February 2016, the danger of ZIKV on pregnancy as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC).
Although accumulating lines of evidence are consistent with observed microcephaly in infected fetuses, there is an urgent need for the development of an animal model to firmly establish the link between vertical ZIKV infection and malformation of the fetal brain.
Recently, a collaborative work between research teams of Dr. LUO Zhenge at Institute of Neuroscience, State Key Laboratory of Neuroscience, Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Dr. QIN Chengfeng at the State Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Biosecurity, Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology, has established the causal link between maternal ZIKV infection and malformation of the fetal brain in a mouse model. They show that maternally infected ZIKV can cross the mouse placental barrier, infect radial glial cells of the fetal brain, and cause either directly or indirectly a reduction in the proliferative pool of cortical neural progenitors, leading to discernable brain developmental defects in offspring mice.
This study thus supports the conclusion that vertically transmitted ZIKV affects fetal brain development and provides a valuable animal model for the evaluation of potential therapeutic or preventative strategies.
This work was published online in Cell Research on May 13th with WU Kongyan, ZUO Guolong, LI Xiaofeng as co-first authors and Dr. LUO Zhenge and Dr. QIN Chengfeng as co-corresponding authors.
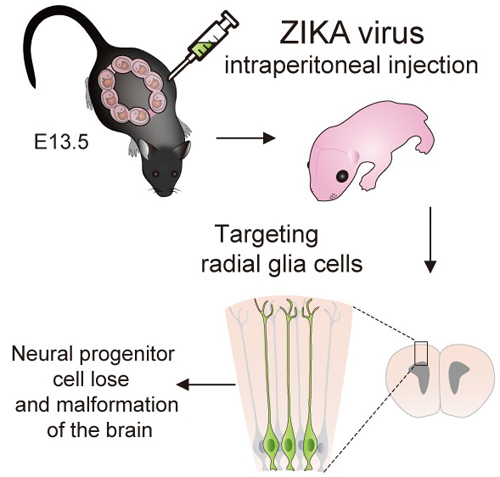
Maternal Zika virus infection affects fetal mouse brain development
 附件下载:
附件下载: