Time:2015-12-29
Somatosensory neuron types were identified by high-coverage single-cell RNA-sequencing and functional heterogeneity, as reported on Dec. 22th in Cell Research. High-coverage single-cell RNA-sequencing was performed to identify neuron types by size-based hierarchical clustering. Physiological functions were determined by the responses of somatosensory neuron to peripheral stimuli recorded by in vivo patch clamp. Then recorded neurons were sorted into neuron types by the identification of representative genes. This study provides a new system for cataloging somatosensory neurons and their transcriptome databases.
Sensory neurons are distinguished by distinct signaling networks and receptive characteristics. Thus, sensory neuron types can be defined by linking transcriptome-based neuron typing with the sensory phenotypes. Gene profiles of individual somatosensory neurons of the mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) were obtained by high-coverage single-cell RNA-sequencing. Then differential expressed genes were identified. Neuron types were identified by neuron size-based hierarchical clustering. Marker genes were also identified by bioinformatic analysis. Moreover, single DRG neurons responding to cutaneous stimuli are recorded using an in vivo whole-cell patch clamp technique and classified by neuron-typegenetic markers. Small diameter DRG neurons are classified into one type of low-threshold mechanoreceptor and five types of mechanoheat nociceptors (MHNs). Each of the MHN types is further categorized into two subtypes. Larg eDRG neurons are categorized into four types, including neurexophilin 1-expressing MHNs and mechanical nociceptors (MNs) expressing BAI1-associated protein 2-like 1 (Baiap2l1). Mechanoreceptors expressing trafficking protein particle complex 3-like and Baiap2l1-marked MNs are subdivided into two subtypes each.
This work entitled a€?Somatosensory neuron types identified by high-coverage single-cell RNA-sequencing and functional heterogeneity " was carried out by Dr. LI Changlin and collaborators under the supervision of Dr. ZHANG Xu at the Institute of Neuroscience, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31130066 and 81300961) and the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB01020300).
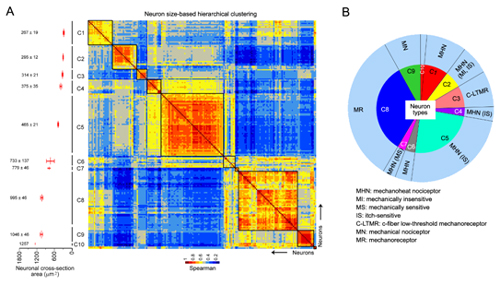
Figure A, A heatmap of size-based hierarchical clustering shows the color-coded correlation matrix of 197 neurons. Ten clusters of strongly correlated neurons are marked with black frames and shown with the given names and their averaged area of neurons to the left.
Figure B, A schematic showing the proposed framework of DRG neuron types and their proportions based on both transcriptomic analysis and ISH, as well as functional annotations suggested by electrophysiological analysis results and published data.
 附件下载:
附件下载: